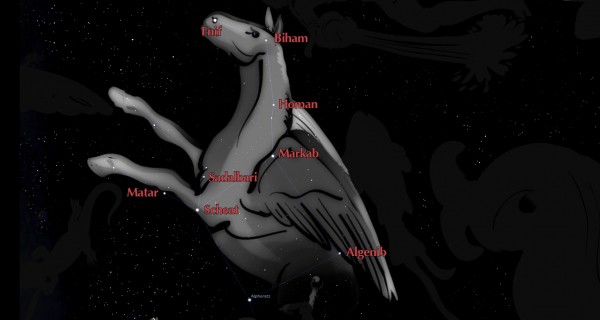
In the Northern section of the sky next to Pisces and Aquarius is the Constellation is Pegasus. Pegasus is named after the mythical winged horse of the Ancient Greeksand named by the astronomer Ptolemy. The asterism The Great Square of Pegasus is made up of four stars Markab, Scheat, Algenib and Alpharatz. There are 8 named stars:
Name: Markab | Bayer Designation: α | Origin: Arabic | Meaning: the saddle of the horse
Name: Scheat | Bayer Designation: β | Origin: Arabic | Meaning: the leg
Name: Algenib | Bayer Designation: Γ | Origin: Arabic | Meaning: the flank
Name: Enif | Bayer Designation: ε | Origin: Arabic | Meaning: nose
Name: Homam | Bayer Designation: ζ | Origin: Arabic | Meaning: man of high spirit
Name: Matar | Bayer Designation: η | Origin: Arabic | Meaning: lucky rain of shooting stars
Name: Biham | Bayer Designation: Θ | Origin: Arabic | Meaning: the livestocks
Name: Sadalbari | Bayer Designation: μ | Origin: Arabic | Meaning: luck star of the splendid one
Markab – Alpha Pegasi (α Peg, α Pegasi) is the third brightest star and is located about 133 light years from Earth and is one of the four stars in the asterism known as the Great Square of Pegasus. The apparent visual magnitude of this star averages 2.48
Scheat – Beta Pegasi (β Peg, β Pegasi) with apparent visual magnitude averaging 2.42, making it the second brightest star in the constellation after Epsilon Pegasi. It is located about 196 light years from Earth and forms the upper right corner of the Great Square.
Algenib – Gamma Pegasi (γ Peg) is located at the lower left-hand corner of the asterism known as the Great Square. The average apparent visual magnitude of +2.84 puts this at fourth place among the brightest stars in the constellation. It is located roughly 390 light-years from Earth.
Enif – Epsilon Pegasi (ε Peg, ε Pegasi) is the brightest star. With an apparent visual magnitude of 2.4,this is a second-magnitude star that is readily visible to the naked eye. It is located roughly 690 light-years from Earth.
Homam – Zeta Pegasi (ζ Peg) a single star with an apparent visual magnitude of +3.4, and is one of the brighter members of Pegasus. Parallax measurements place it at a distance of around 204 light-years (63 parsecs) from Earth. The radius of this star is about four times that of the Sun
Matar – Eta Pegasi (η Peg) is a binary star with the apparent visual magnitude of this star is +2.95, making this the fifth brightest member of Pegasus. Based upon parallax measurements, the distance to this star is about 167 light-years (51 parsecs). This system consists of a pair of stars in a binary orbit with a period of 813 days and an eccentricity of 0.183.
Biham – Theta Pegasi (θ Peg) is a star of spectral class A2 and has apparent magnitude +3.53. It is approximately 67 light years from Earth. This star has 2.6 times the Sun’s radius and it is radiating 25 times the luminosity of the Sun from its outer envelope at an effective temperature of 7,951 K.
Sadalbari – Mu Pegasi (μ Peg, μ Pegasi) is a star with the apparent visual magnitude of 3.5, which is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye even on a moonlit night. The distance to this star can be determined with parallax measurements, which yields a value of 106.1 light-years (32.5 parsecs).
Glossary
planet – A planet is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. A dwarf planet is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, (c) has not cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit, and (d) is not a satellite. All other objects, except satellites, orbiting the Sun shall be referred to collectively as “small solar system bodies”.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.